The U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry Security, and E5 Partners Provide Guidance and Export Controls on Russia
Bradley Intelligence Report
In a coordinated effort to counter Russia's aggression against Ukraine, the Export Enforcement Five (E5) — comprising Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States — have released unprecedented packages of sanctions and export controls. These measures aim to impose economic costs on Russia, degrade its war capabilities, and show solidarity with Ukraine. For businesses, failure to understand the evolving export controls sanctions environments and conduct due diligence on partners can result in reputational harm, future business relationship challenges, fines, and/or criminal charges. This analysis aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the guidance issued by the Bureau of Industry Security (BIS), the E5, and the Exporting Commercial Goods Guidance for Industry and Academia.
The E5 Partnership and GECC
The E5 partnership was established to enhance the effectiveness of each country's export control regimes and is administered in coordination with the 39-member Global Export Control Coalition (GECC). The E5's coordinated efforts have significantly hindered Russia's ability to wage its illegal war in Ukraine and have forced Russian officials to make difficult economic choices.
New Export Control Restrictions
Since February 2022, the Bureau of Industry Security (BIS), in coordination with its E5 partners, imposed new export control restrictions aimed at cutting off Russia’s access to critical components used for aircraft, tanks, semiconductors, and other items needed for advanced military applications, and low-technology consumer goods needed for Russia to sustain the war in Ukraine.
These new restrictions, comprise of four rules, revise the Commerce Department’s Export Administration Regulations (EAR) to enhance existing controls and add hundreds of low-level items to the United States’ Russia export control; impose controls on specific items destined for Iran, including semiconductors that are components for Iranian Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) used by Russia in Ukraine; and add several entities to the BIS Entity List.
High-Priority Items List for Russian Weapons Systems
The E5’s High Priority Items List is primarily based on the Harmonized System (HS) Code classification of Russian weapons system components recovered on the battlefield in Ukraine. Items described by these HS codes have been found in multiple Russian weapons systems used against Ukraine, including the Kalibr cruise missile, the Kh-10 cruise missile, and the Orlan-10 UAV.
The E5, in collaboration with international partners, including the EU and Japan, has prioritized controlled items in a list of 45 HS codes. These codes include electronic components such as integrated circuits and radio frequency (RF) transceiver modules critical to Russian weapons systems. The list is divided into four tiers, ranked according to their criticality:
- Tier 1: Integrated circuits (microelectronics)
- Tier 2: Electronics related to wireless communication, satellite-based radio navigation, and passive electronic components
- Tier 3: Divided into electronic and non-electronic items to provide greater clarity to the different industries that may work with these items
- Tier 4: Manufacturing, production, and quality testing equipment of electric components and circuits
Risk-Based Approach to Exporting
Exporters are strongly encouraged to conduct due diligence when encountering listed HS codes. BIS suggests exporters use additional due diligence when encountering one of the nine Tier 1 or Tier 2 HS codes, reproduced below:
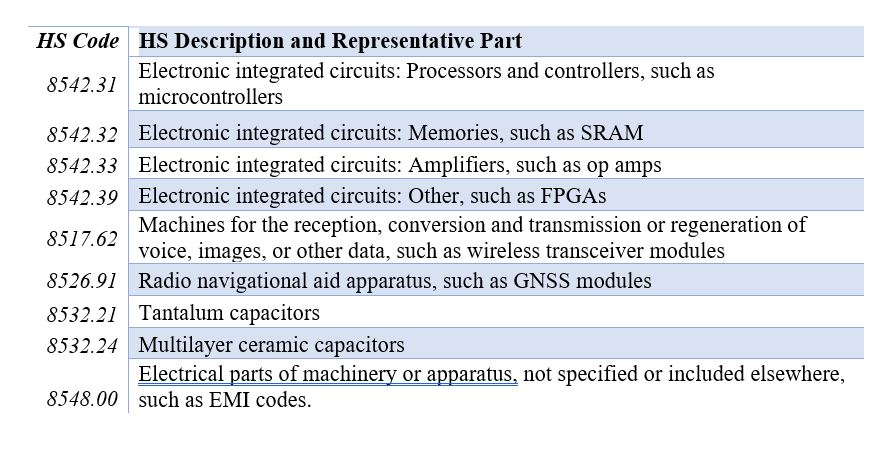
Three patterns have been identified that raise diversion concerns regarding the Tier 1 and Tier 2 HS Codes:
- The company never received exports prior to February 24, 2022.
- The company received exports that did not include Tier 1 and Tier 2 HS codes before February 24, 2022.
- The company saw a significant spike in exports involving the nine Tier 1 and Tier 2 HS codes after February 24, 2022.
Red Flag Indicators
The E5 has provided a list of potential red flag indicators for export controls and sanctions evasion. These include:
- Transactions related to payments for defense or dual-use products from a company incorporated after the Russian invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022, and based in a non-GECC country.
- A new customer whose line of business is in the trade of products associated with the Tier 1 or Tier 2 HS codes was incorporated after February 24, 2022.
- An existing customer who did not receive exports associated with the Tier 1 or Tier 2 HS codes prior to February 24, 2022, and is now exporting or re-exporting such items to known transshipment points.
The complete list of red flags can be found here.
Responsibilities and Resources for Exporters
Failure to comply with these recommendations can result in reputational harm, future business relationship challenges, fines, and/or criminal charges. Exporters are urged to consult various screening tools and resources available for preliminary compliance and due diligence, such as the Consolidated U.S. Screening Tool, OFAC Sanctions List Search, and BIS Policy Guidance. The joint guidance and export controls issued by the E5 and GECC are a significant milestone in international efforts to counter Russia's evasion tactics. They provide a comprehensive framework for industry and academia to align their activities with the broader goals of preventing the diversion of critical items to Russia. Compliance with these guidelines is a legal requirement and a moral imperative in the global effort to curb Russia's aggressive actions.


